SQL Secure
Strengthen SQL Server Security with Automated Risk Insights
Protect your databases across Microsoft SQL, Azure and Amazon RDS with automated security alerts to safeguard your sensitive information from potential threats
Why SQL Secure?
SQL Secure dramatically reduces the complexity and manual effort required to analyze, audit, and manage SQL Server security. It allows Database Administrators (DBAs) to confidently answer the critical question: “Who has access to what, where, and how?”—across on-premises and cloud-based SQL Server environments.
Managing SQL Server security is increasingly difficult due to:
- Complex and inconsistent permission structures
- Limited visibility into user and group access rights
- Risk of privilege escalation and insider threats
- Inability to easily meet security audit requirements
- Difficulty enforcing consistent security policies across environments
SQL Secure delivers a comprehensive solution for analyzing, monitoring, and reporting on SQL Server security access. With features like role-based analysis, the Security Report Card, and built-in templates for compliance, DBAs can quickly identify vulnerabilities, enforce least-privilege access, and stay audit-ready at all times.
SQL Secure Features and Benefits
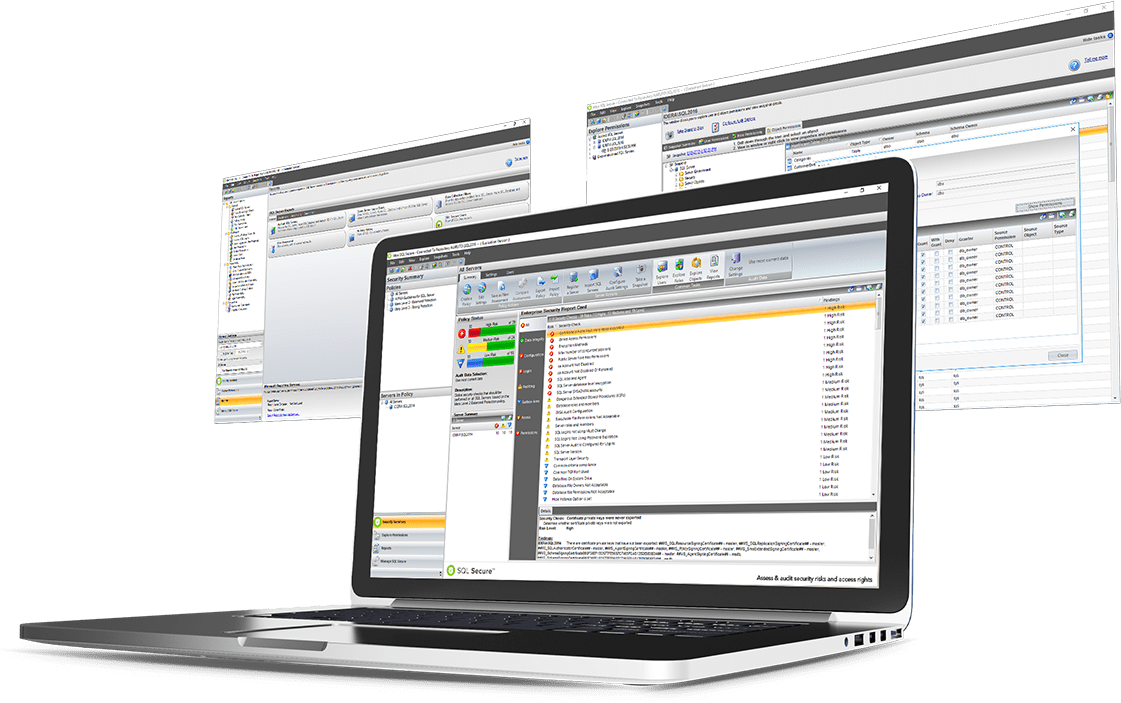
SQL Server Security Analysis
- ✓ Analyze user access paths and effective permissions across roles, servers, and databases.
- ✓ Detect weak or blank passwords, unresolved accounts, and over-privileged users.
- ✓ Assess server and OS-level security settings, including ports, protocols, and authentication modes.
SQL Server Security Reporting
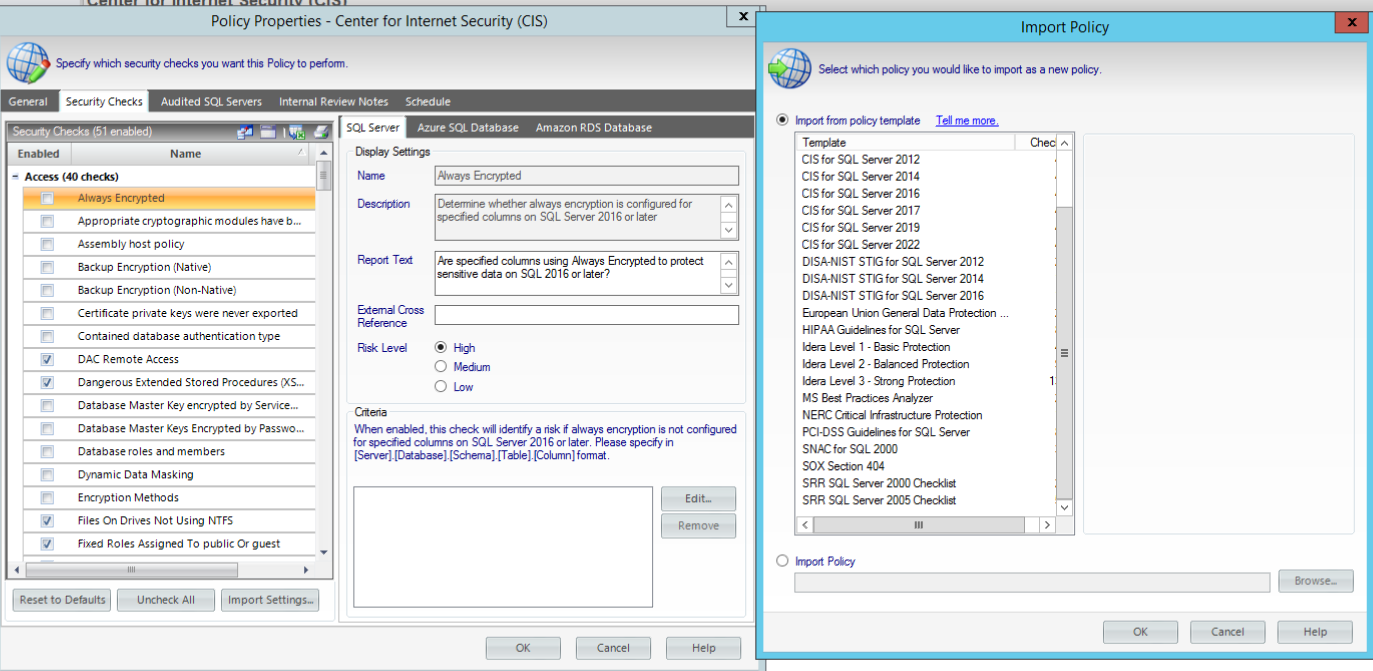
- ✓ Use policy templates to assess security strength with basic, balanced, or strong audit levels.
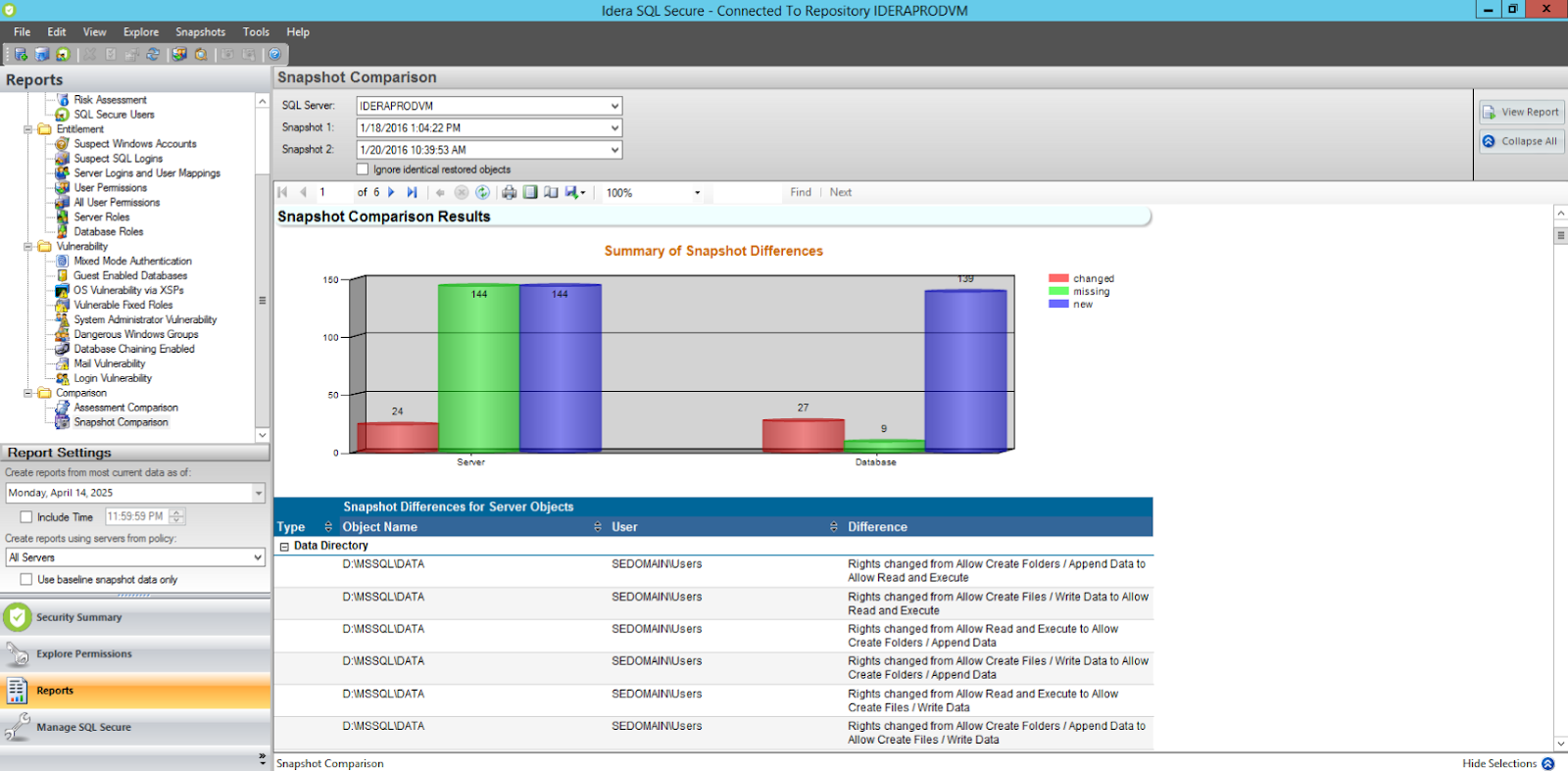
- ✓ Generate detailed reports, including customizable outputs and a visual security scorecard.
- ✓ Track historical changes to security settings with baseline comparisons across servers.
- ✓ Audit risk with checks for permissions, configuration and encryption.
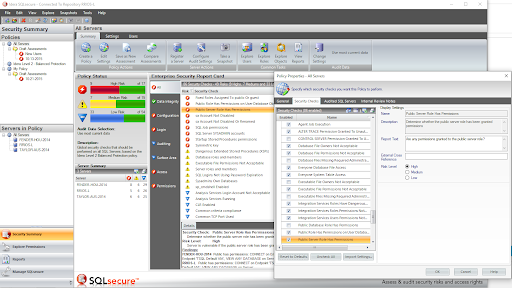
Enterprise Reporting
- ✓ Review policies, risk assessments and user permissions from a single console
- ✓ Configure and schedule security data collection across physical, virtual, and cloud environments.
- ✓ Store all collected security data in a central repository for streamlined reporting and auditing.
- ✓ Organize servers with flexible grouping, tagging and automated registration
Cloud
- ✓ Install and run SQL Secure on cloud VMs, including Azure VM and Amazon EC2.
- ✓ Monitor SQL Server on physical, virtual, and cloud platforms from a single tool.
- ✓ Extend coverage to managed cloud databases like Azure SQL Database and Amazon RDS.
Download a 14-day Free Trial!
Auditing is made easy with SQL Secure. Get a two-week, fully functional free trial and put SQL Secure to work for your organization.
SQL Secure Works For…
Enterprise
- ✓ Centralized security policy management and permission analysis across large SQL Server environments.
- ✓ Automated data collection from hybrid infrastructures including physical, virtual, and cloud servers.
- ✓ Scalable architecture supports complex topologies and high volumes of SQL instances.
- ✓ Central repository for consolidated reporting and long-term security audits.
- ✓ Scalable architecture to support hundreds or thousands of SQL Server instances.
- ✓ Comprehensive risk assessments and policy enforcement from a single, unified console.
Teams
- ✓ Streamlined onboarding of multiple servers with automated rule and policy templates.
- ✓ Role-based access to enforce internal governance and compliance controls.
- ✓ Group tagging and flexible views to organize, monitor, and secure server clusters.
- ✓ Powerful reporting and scorecards to track risks and communicate findings across teams.
- ✓ Simplified analysis of user permissions, roles, and effective rights across shared environments.
Single Users
- ✓ Visual dashboard for fast access to permissions, risks, and audit history.
- ✓ Predefined security policies to jumpstart analysis and compliance checks.
- ✓ Drill-down capabilities to uncover vulnerabilities like blank passwords or open ports.
- ✓ Lightweight, agentless architecture for low-impact assessments.
- ✓ Easy export and report generation to share insights or maintain documentation.