Purpose of this document
Due to its depth and potential for customization, there are often parts of Idera SQL Defrag Manager that are overlooked during the initial trial period. This document is designed to point out areas that may have been missed or that can be modified to give you full control over management and reporting in your SQL Server environment.
Introduction
SQL Defrag Manager lets you find and fix fragmentation hot spots on databases running in your SQL Server environment.
Why use Defrag Manager?
- Automated analysis – Analysis of over 20 key metrics to pinpoint fragmentation hot spots
- Intelligent remediation – Intelligent heuristics determine the best-fit approach and schedule for defragmentation, ensuring the minimum impact to production servers
- Continuous improvement – Analysis of historical fragmentation statistics enables SQL Defrag Manager to intelligently refine its approach as time progresses
- Centralized management – Management console provides central management and control of defragmentation activity across hundreds of servers
- Granular retrospective analysis – Drill down to a point-in-time snapshot and see what was causing system issues
- Comprehensive reporting – Easily run reports to verify that database performance is continuously optimized
- Resource monitor – Postpone defrag operations when resource contention issues are discovered
- Automated alerting – Email alerts help inform administrators of fragmentation issues and policy results
- Immediate feedback and automated responses – Alerts when there are issues & automates responses to common problems
- Easily adjusted policies – Use “set it and forget it” policies to easily adjust how you handle your fragmentation issues
System requirements
- Windows 2000 SP4, Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows 2008 SP1, Windows Vista SP2+, Windows 7 SP1+, Windows 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows 2012
- Microsoft .NET 2.0 SP1
- MDAC 2.8 or later
- Windows Installer 3.1 or later
- Windows 2000 SP4, Windows XP SP3, Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows 2008 SP1, Windows Vista SP2+, Windows 7 SP1+, Windows 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows 2012
- Microsoft .NET 2.0 SP1
- Repository: SQL Server 2000, 2005, 2008, 2008 R2, 2012
- SQL Server 2000 and SQL Server 2005
- SQL Server 2008 R2
- SQL Server 2012
- SQL Server 2014
Management Service Permission Requirements
The Windows user account used by the Management Service requires the following permissions to access the SQL Server instances you want to manage:
| TYPE | REQUIREMENT |
|---|---|
|
Windows permissions
|
Local Administrator permissions on the computer hosting the Management Service.
|
|
SQL Server Privileges
|
A member of the sysadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance hosting the Repository and on each managed SQL Server instance.
|
Product components
The SQL Defrag Manager Console is the interface you use to configure SQL Defrag Manager, view analysis and defragmentation results, schedule automation activities, and perform other related functions.
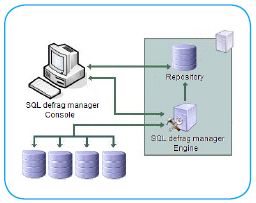
The SQL Defrag Manager Repository is a central storage area for configuration information & fragmentation data and statistics collected by the Management Service.
The SQL Defrag Manager Management Service gathers fragmentation data from your managed SQL Server instances and stores the information in the SQL Defrag Manager Repository database. The Management Service also controls scheduling activities.
The managed instances are the SQL Server instances you registered with SQL Defrag Manager. SQL Defrag Manager periodically analyzes and optimizes these instances based upon the management settings you specified. SQL Defrag Manager stores this collected data in the SQL Defrag Manager Repository and displays the data in the SQL Defrag Manager Console.
SQL Defrag Manager Capabilities
- Click Register on the Fragmentation Explorer tab of the SQL Defrag Manager Console or click next on the Welcome window.
- Follow the instructions until you finish registering the SQL Server instances you want to manage. This wizard allows you to select the:
- A. Instances to register
B. Authentication type
C. Policy
Automate defragmentation using policies
You can use SQL Defrag Manager to analyze database index fragmentation across your enterprise. You can then defragment hot spots to improve performance. SQL Defrag Manager provides policies that allow you to automate this process and maintain your databases with minimal time and effort.
Automate defragmentation using policies
You can use SQL Defrag Manager to analyze database index fragmentation across your enterprise. You can then defragment hot spots to improve performance. SQL Defrag Manager provides policies that allow you to automate this process and maintain your databases with minimal time and effort.
- Select the indexes you want to evaluate.
- Select the index thresholds and analysis frequency.
- Select index filter options.
- Select policy response.
- Schedule when and how often you want the policy to run.
- Select which resource checks to run before running the policy.
- Select the action you want to occur when certain conditions are met.
- Select the action you want to occur when certain conditions are met.
- Name the policy.
Perform manual defragmentation
When you initially use SQL Defrag Manager, you should first analyze your databases to collect updated fragmentation information. Then, review that information and defragment the highly-fragmented areas. As you become familiar with SQL Defrag Manager, you may choose to automate this process. This section describes how to manually analyze, view, and correct fragmentation issues on tables and indexes. Use the following topics to guide you through the manual defragmentation process.
- Analyze database fragmentationt
The SQL Defrag Manager Analyze Fragmentation window allows you to investigate the fragmentation levels of tables and indexes in the registered databases and instances. The SQL Servers and Databases field lists all the registered instances and databases. Select one or more database for analysis, specify the type of analysis you want SQL Defrag Manager to perform, and then click Finish. - View analysis results
Once SQL Defrag Manager analyzes the registered instances and databases, you can use the Fragmentation Explorer tab to view the latest analysis information. SQL Defrag Manager displays the analysis details for the objects within the selected database object. For example, if you select a table, SQL Defrag Manager displays the analysis details for each index on that table.
You should regularly monitor fragmentation levels on indexes and schedule SQL Defrag Manager to regularly analyze database fragmentation. Use the scheduled analysis to identify specific fragmentation levels before defining your policies to automatically reorganize or rebuild indexes. - Optimize performance and space usage
The Defragment and Optimization window allows you to defragment one or more instances and databases. The SQL Servers and Databases field lists all the registered instances and databases. You can select the databases you want to defragment, and then select the type of defragmentation approach you want to use. SQL Defrag Manager simply reorganizes indexes for optimal performance or defragments indexes by completely rebuilding them.
View activity and results
After an action occurs, you can view alert history (if configured) and the recent activities occurring in your environment, and you can run reports to compile and display the available information. All of this data helps you verify that your policies are effective and that you are using SQL Defrag Manager most effectively. Use the following topics to help you decide what information you want to view:
- View Alert History
If you configured policies to send alerts, SQL Defrag Manager displays a record of those alerts on the Alerts History tab. - View Recent Activity
The Recent Activity tab of the SQL Defrag Manager Console displays the analysis and defragmentation tasks SQL Defrag Manager has performed. You can view the improvements accomplished during each defragmentation task. - View Reports
Once you have configured SQL Defrag Manager and assigned policies, you can run reports to compile and display the information available. You can access these reports by clicking the Reports tab.
Once you have configured SQL Defrag Manager and assigned policies, you can run reports to compile and display the information available. You can access these reports by clicking the Reports tab.
You can select from the following list of reports:
- All Registered Objects
Shows all registered objects in SQL Defrag Manager (servers, databases, tables, indexes, and partitions), whether they are scheduled for automated analysis or defragmentation. - Index Counts
Shows index counts by server, database, and table registered with SQL Defrag Manager. - Page Density Change Over Time
Shows page density changes as a result of index and partition operations over time, filtered by server, database, and minimum page count. - Resources Reclaimed Over Time
Shows the number of pages reclaimed over time using SQL Defrag Manager for each server, database, index, and partition. - Top 10 Fragmented Clustered Indexes
Shows a list of the top 10 clustered indexes with the greatest amount of fragmentation. - Top 10 Fragmented Indexes
Shows a list of the top 10 indexes with the greatest amount of fragmentation. - Top 10 Largest Databases
Shows a list of the top 10 largest databases ordered by the sum of the last analyzed index page counts. - Top 10 Largest Indexes
Shows a list of the top 10 largest indexes ordered by the last analyzed index page counts. - Top 10 Largest Tables
Shows a list of the top 10 largest tables ordered by the sum of the last analyzed index page counts.